Basic Hair Structure Hair Follicle and Hair Shaft Function
Table Of Content
At the isthmus level, epithelium keratinization begins with the lack of granular layer named “trichilemmal keratinization” [14, 16]. Only few differentiated corneocytes remain and the invagination of the epidermis in this area must be considered as highly permeable for topically applied compounds [19]. Hair follicle stem cells are thought to reside in the bulge area on the isthmus close to the insertion of the arrector muscle [20]. Lineage studies have proven that bulge cells are multipotent and that their progeny generate the new lower anagen hair follicle [21]. On entering the hair bulb matrix, they proliferate and undergo terminal differentiation to form the hair shaft and inner root sheath. They also migrate distally to form sebaceous glands and to proliferate in response to wounding [16, 20, 22].
Basic Hair Structure and function
In this stage, stem cells from the bulge in the follicle multiply and travel downward, pushing the dermal papilla deeper into the skin and forming the epithelial root sheath. Root sheath cells directly above the papilla form the hair matrix. Here, sheath cells transform into hair cells, which synthesize keratin and then die as they are pushed upward away from the papilla. The new hair grows up the follicle, often alongside an old club hair left from the previous cycle. Strands of hair originate in an epidermal penetration of the dermis called the hair follicle.
Hair shaft
Robert Pattinson's Hair Is Glorious—8 Tips to Get His Hairstyle - Men's Health
Robert Pattinson's Hair Is Glorious—8 Tips to Get His Hairstyle.
Posted: Thu, 03 Sep 2020 07:00:00 GMT [source]
This gives your hair shine and protects the inner layers from damage. It also minimises the movement of moisture in and out of the underlying cortex, thus maintaining your hair’s hydration balance and flexibility. However, chemical processes and weathering can lift the cuticle and disrupt this balance, causing your hair to become dry and brittle.
Blood Supply and Lymphatics
The medulla is a core of loosely arranged cells and air spaces. It is most prominent in thick hairs such as those of the eyebrows, but narrower in hairs of medium thickness and absent from the thinnest hairs of the scalp and elsewhere. However, a lot of vellus hair turns into terminal hair (which includes eyebrows, eyelashes and scalp hair). And male hormones (androgens) also stimulate vellus hair to "mature" into facial hair, body hair and pubic hair.
Medulla
Hair Gloss vs. Hair Dye: Hairstylists Explain the Difference - Women's Health
Hair Gloss vs. Hair Dye: Hairstylists Explain the Difference.
Posted: Tue, 19 Apr 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
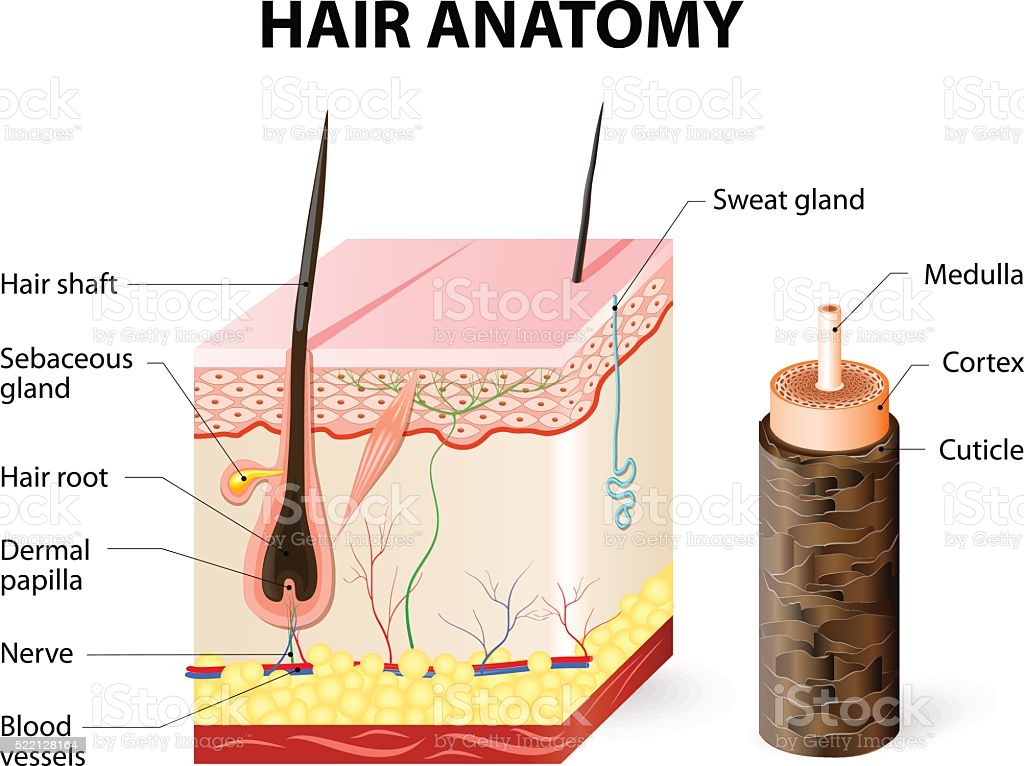
Again, the hair follicle shows four different important layers – inner root, outer root, a glassy membrane, and a well-vascularized connective tissue layer. The wall of the hair follicle is made of three concentric layers of cells. The cells of the internal root sheath surround the root of the growing hair and extend just up to the hair shaft. The external root sheath, which is an extension of the epidermis, encloses the hair root. It is made of basal cells at the base of the hair root and tends to be more keratinous in the upper regions. The glassy membrane is a thick, clear connective tissue sheath covering the hair root, connecting it to the tissue of the dermis.
The Biology, Structure, and Function of Hair
The ones located in several areas like scalp, eyebrows and eyelashes are thicker, longer and pigmented and are called terminal hairs. Humans have approximately 5 million hair follicles and 100,000 of them are located on the scalp [11] (Table 2) [2]. After that, an increasing percentage of follicles are in the catagen and telogen phases rather than the growing anagen phase. Hair follicles also shrink and begin producing wispy vellus hairs instead of thicker terminal hairs. It occurs to some degree in both sexes and may be worsened by disease, poor nutrition, fever, emotional stress, radiation, or chemotherapy.
Structure of Hair Follicle
A root hair plexus of sensory nerves surrounds the base of each hair follicle. This sensitivity gives an early-warning system that may help prevent injury. For example, stimulation of the hair receptors, however, alerts people to parasites crawling on the skin, such as fleas and ticks, and to remove them.
Observing the hair shaft under a light microscope of an animal or human hair will find this cortical fusi near the root of mature hair. You will also find this cortical fusi throughout the hair shaft of different animals and humans. There is no inner root layer at the neck of the hair follicle where the ducts of the sebaceous gland open into the hair follicle. So, if you want to know the microscopic features of the animal hair shaft and hair follicles, let’s continue this article till the end.
The shedding period is believed to be an active process and independent of telogen and anagen thus this distinct shedding phase is named exogen [16, 33]. The macro-environment surrounding the hair follicle also takes part in regulating cycle transitions. Thus hair follicle IP is limited to the proximal epithelium of anagen hair follicles.

If it is lost or damaged, the hair will look dull and become brittle because the cells in the cortex may break and unravel. The sebaceous gland is important because it produces sebum which is a natural hair conditioner. The sebum production decreases in women throughout their lives.
Several molecular pathways, growth factors, proteins and genes play substantial roles for the development of the hair follicle. Activation of this β-catenin pathway seems to be essential for the epithelial ability of the hair follicle production [7]. Hair, in mammals, the characteristic threadlike outgrowths of the outer layer of the skin (epidermis) that form an animal’s coat, or pelage. On adult whales, elephants, sirenians, and rhinoceroses body hair is limited to scattered bristles. In most other mammals the hair is abundant enough to form a thick coat, while humans are among the most hairless of all mammals.
When they reach the upper part of the bulb, they arrange themselves into six concentric layers. The three inner layers become the hair, made up of the cuticle, the cortex and the medulla (although the medulla isn’t always present, especially in hairs with a thinner diameter). The telogen stage is defined as the duration between the completion of follicular regression and the onset of the next anagen phase. During the telogen stage, the hair shaft is transformed to club hair and finally shed. Nearly whole body surface is coated with the hairs except a few areas like palms, soles and mucosal regions of lips and external genitalia.
Comments
Post a Comment