Hair Shaft, Follicle, Structure, Hair Bulb Root & Function
Table Of Content
Thus, you are less likely to become unknowingly infested with parasites. The 5 million hairs on the human body have important functions. Most hair of the human trunk and limbs is probably best interpreted as vestigial, with little present function. The roughly 100,000 hairs on the head protect the scalp from ultraviolet light and bumps to the head and insulate the skull.
Hair and follicle morphology
I tried my best to provide a perfect guide with possible explanations, labeled images, and videos to learn gross veterinary anatomy and histology of animal’s organs. The rabbit hair is extremely used in felted fabrics, gloves linings, fur trim, coats, and others. I tried to show you the different parts of the cattle’s hair shaft in the diagram.
Hair Loss Myths Debunked
The anagen is the active growth phase in which the follicle enlarges and takes the original shape and the hair fiber is produced. Outer root sheath (ORS) extends from the epidermis at the infundibulum and continues to the hair bulb and its cells change considerably throughout the follicle. In the infundibulum, it resembles epidermis, whereas in the isthmus level, ORS cells begin to keratinize in a trichilemmal mode. Keratinocytes in the ORS form the bulge area at the base of the isthmus.
In brief: What is the structure of hair and how does it grow?
This Body-Hair Ambassador Is Validating The Natural Look - Men's Health
This Body-Hair Ambassador Is Validating The Natural Look.
Posted: Tue, 20 Sep 2022 07:00:00 GMT [source]
This allows capillaries (blood vessels) to enter the papilla and provide nutrients for the hairshaft to grow. At the end of the growth phase, the hair root separates from the papilla. Then a transitional phase called the catagen phase starts, lasting about two to four weeks.
These coronal scales are mainly found in the hair shaft of rodents and bats. But, you may rarely find this type of scale in the hair shaft of humans. But, you need to know the basic structure of the hair first, including different parts, structures of the hair shaft, and follicles. You will also find the difference in the hair roots of a human and animals. In a dog, you will often find a spade-shaped hair root, whereas a cat shows frayed at the base of their hair.
9 Hair Trends That Will Be Everywhere In 2024, According To Experts - Women's Health
9 Hair Trends That Will Be Everywhere In 2024, According To Experts.
Posted: Tue, 02 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
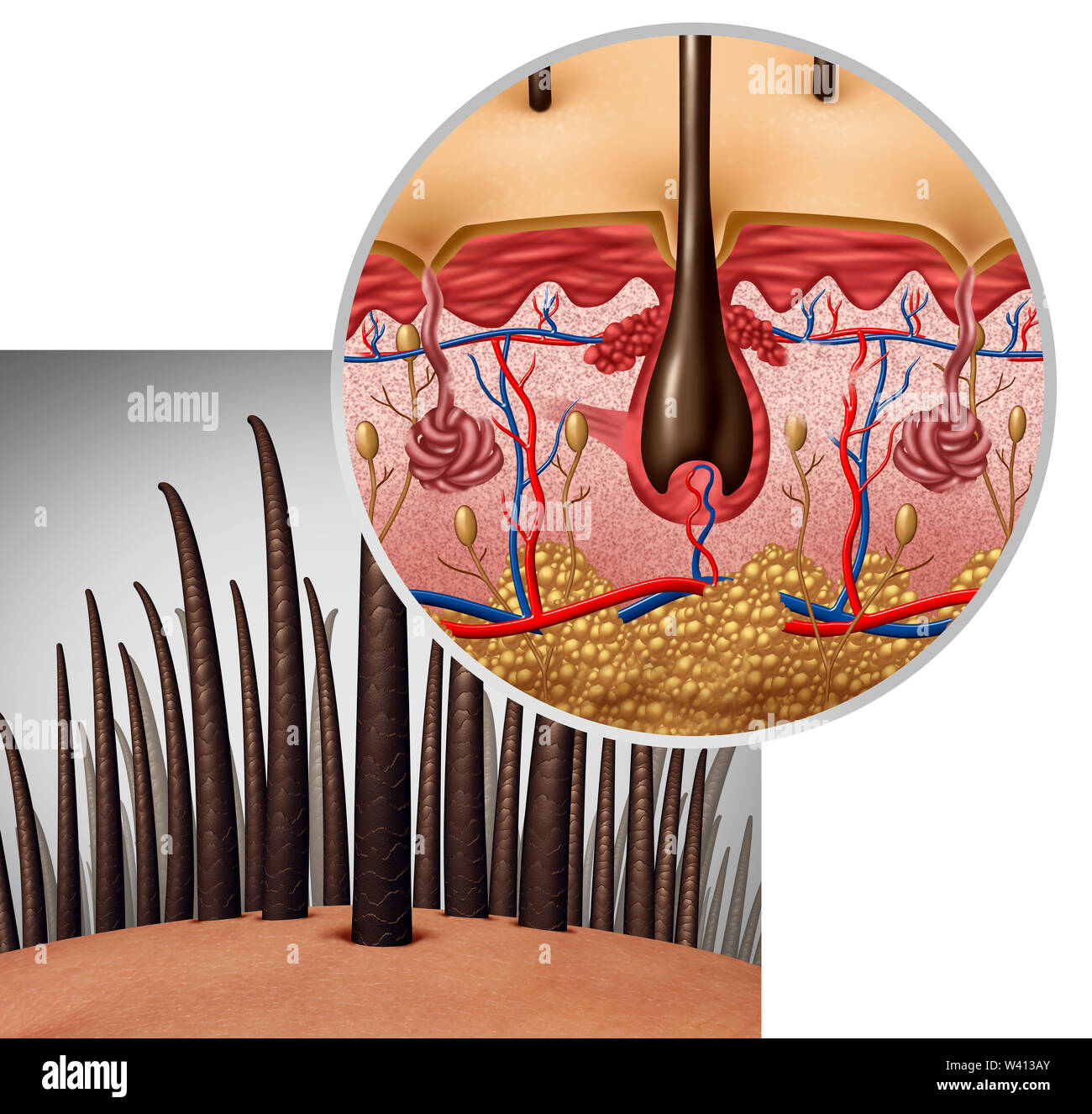
Again, the outermost cell layers of the outer layer and the lowest layer of cells of the hair bulb represent the basal cell layers of the epidermis. Under the light microscope, hair follicles may be seen as the epidermis part that enters into the dermis around the hair root. The innermost layer that immediately surrounds the hair root is therefore continuous with the surface of the skin. Again, the outermost layer of the follicle is continuous with the dermis. Cutaneous vascularization is provided by arterioles, which are concentrated at the lower portion of the hair follicle and compose vascular network. During the hair cycle phases, there are some alterations in the density of perifollicular vascularization due to the upregulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression [1].
Hair follicle
Hair is at its most delicate when wet, as it stretches when being combed and can easily snap or break, resulting in split ends. Because of its bipolar properties shea will hold water to the shaft, and asist with medullary moisture homeostasis at the same time shea help regulate sebum production in the scalp. The healthy hair of any animal consists of a hair shaft and hair follicle. Again, the shaft of healthy hair comprises of cuticle, cortex, and medulla. The microscopic figure of the healthy hair shows overlaying scales.
Dog hair under a microscope
There are columns of keratinized cells that organize into three layers in the shaft of a hair. These three layers are – a central medulla, a keratinized cortex, and a thin hard outer cuticle. The outer cuticle is a highly keratinized structure in the hair shaft. Ectodysplasin (EDA) and its receptor (EDAR) are another important pathways involved in the placode stage of hair morphogenesis. In the placode stage, activated WNT and EDAR control the localized accumulation of sonic hedgehog (SHH), which is essential for the downgrowth of the hair germ [2].
How to get rid of uneven skin tone
In the diagram, you will see the longitudinal view of the coronal scales of goat hair. Hair follicles originate in the epidermis and have many different parts. If you are worried about any form of hair or scalp condition, our Clinics in London and New York specialise in all aspects of hair and scalp health, and will be pleased to welcome you. The aim of this chapter is to enhance the knowledge of the complex anatomy and physiology of the hair in a simple manner (Table 1) [2, 5].
The medullary index for the animal hair is usually greater than 0.5. But, you may also see the stacked medulla in some of the hairs. Another name for the discontinuous medulla is broken or interrupted medulla. The proximal end of the hair shaft closes to the scalp, whereas the distal end is farthest from the scalp. The hair root is always attached to the dermis obliquely; thus, the existing hair of the skin is also oblique and easily lies flat on the skin surface. The actions of EDA/EDAR and WNT promote placode formation, whereas BMP signaling represses placode fate in adjacent skin [6].
So, in a cross-section of hair, you will see round (straight hair), oval (curly), and crescent-shaped (kinly). Well, sebum consists of various lipids, including triglycerides, cholesterol, cholesterol ester, and fatty acid. The secretion of the sebaceous gland also prevents the dryness of the skin and makes it resistant to moisture.
A ribbon of smooth muscle, the arrector pili muscle, extends from the papillary layer of the dermis to the connective tissue sheath surrounding the hair follicle. When stimulated, the arrector pili muscle pulls on the follicle and raises the hair. Although we do not receive any comparable insulating benefits, the reflex persists. Genes determine hair color by directing the type and amount of pigment that epidermal melanocytes produce. Variations in hair color reflect differences in hair structure and in the pigment produced by melanocytes at the papilla. Hormonal or environmental factors may influence the condition of your hair.
Comments
Post a Comment